Applications
Diagnostic testsedit
Once monoclonal antibodies for a given substance have been produced, they can be used to detect the presence of this substance. Proteins can be detected using the Western blot and immuno dot blot tests. In immunohistochemistry, monoclonal antibodies can be used to detect antigens in fixed tissue sections, and similarly, immunofluorescence can be used to detect a substance in either frozen tissue section or live cells.
Analytic and chemical usesedit
Antibodies can also be used to purify their target compounds from mixtures, using the method of immunoprecipitation.
Therapeutic usesedit
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies act through multiple mechanisms, such as blocking of targeted molecule functions, inducing apoptosis in cells which express the target, or by modulating signalling pathways.
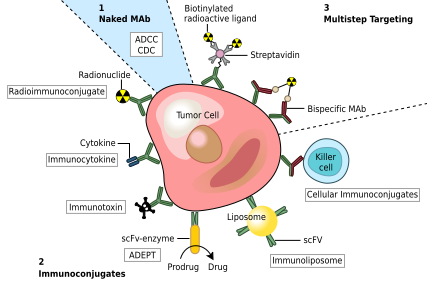
Cancer treatmentedit
One possible treatment for cancer involves monoclonal antibodies that bind only to cancer-cell-specific antigens and induce an immune response against the target cancer cell. Such mAbs can be modified for delivery of a toxin, radioisotope, cytokine or other active conjugate or to design bispecific antibodies that can bind with their Fab regions both to target antigen and to a conjugate or effector cell. Every intact antibody can bind to cell receptors or other proteins with its Fc region.
MAbs approved by the FDA for cancer include:
Autoimmune diseasesedit
Monoclonal antibodies used for autoimmune diseases include infliximab and adalimumab, which are effective in rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and ankylosing spondylitis by their ability to bind to and inhibit TNF-α. Basiliximab and daclizumab inhibit IL-2 on activated T cells and thereby help prevent acute rejection of kidney transplants. Omalizumab inhibits human immunoglobulin E (IgE) and is useful in treating moderate-to-severe allergic asthma.
Examples of therapeutic monoclonal antibodiesedit
Monoclonal antibodies for research applications can be found directly from antibody suppliers, or through use of a specialist search engine like CiteAb. Below are examples of clinically important monoclonal antibodies.
| Main category | Type | Application | Mechanism/Target | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti- inflammatory |
infliximab |
|
inhibits TNF-α | chimeric |
| adalimumab |
|
inhibits TNF-α | human | |
| basiliximab |
|
inhibits IL-2 on activated T cells | chimeric | |
| daclizumab |
|
inhibits IL-2 on activated T cells | humanized | |
| omalizumab |
|
inhibits human immunoglobulin E (IgE) | humanized | |
| Anti-cancer | gemtuzumab |
|
targets myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 on leukemia cells | humanized |
| alemtuzumab |
|
targets an antigen CD52 on T- and B-lymphocytes | humanized | |
| rituximab |
|
targets phosphoprotein CD20 on B lymphocytes | chimeric | |
| trastuzumab |
|
targets the HER2/neu (erbB2) receptor | humanized | |
| nimotuzumab |
|
EGFR inhibitor | humanized | |
| cetuximab |
|
EGFR inhibitor | chimeric | |
| bevacizumab & ranibizumab |
|
inhibits VEGF | humanized | |
| Anti-cancer and anti-viral | bavituximab |
|
immunotherapy, targets phosphatidylserine | chimeric |
| Other | palivizumab |
|
inhibits an RSV fusion (F) protein | humanized |
| abciximab |
|
inhibits the receptor GpIIb/IIIa on platelets | chimeric |
Comments
Post a Comment